We asked you for your Top 30 battles that you would like to see included free with General Staff for supporters of our Kickstarter campaign. We have previously announced the first twenty vote-getters. Today we are announcing the next five. One of the interesting features of General Staff is the ability to combine any two armies with a map to create a scenario. We use this feature for two day battles (such as Wagram and 2nd Bull Run) effectively creating two completely different battles (with two different armies) but using the same battlefield map.
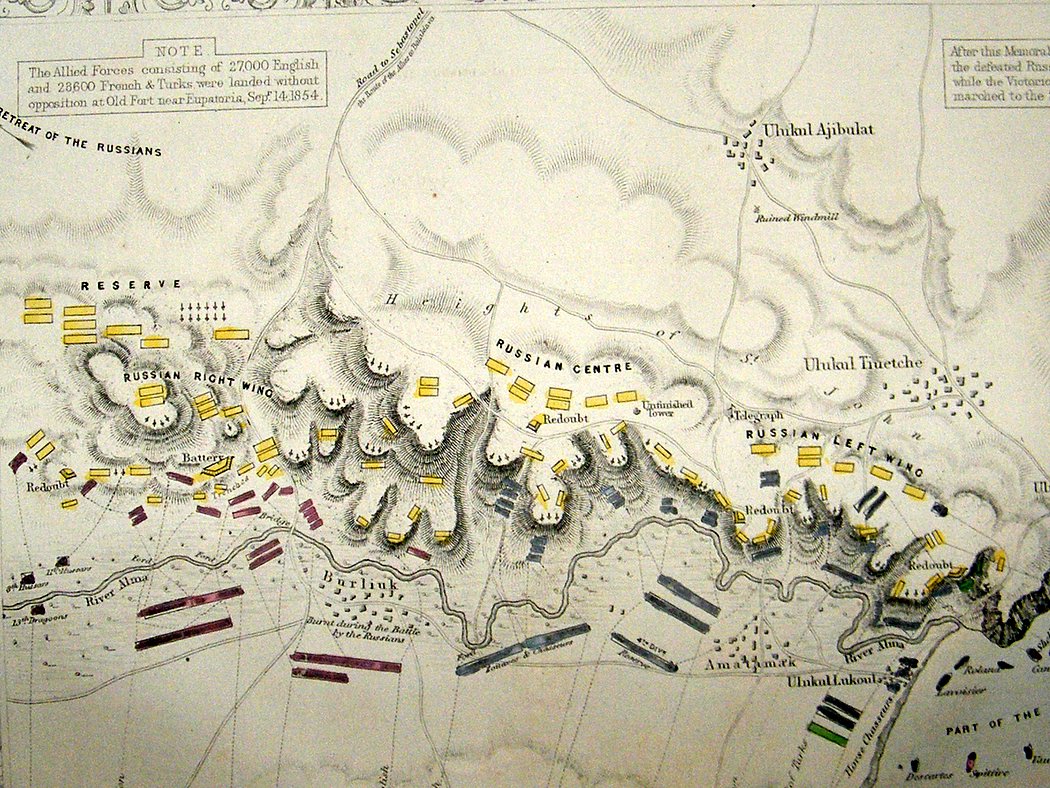
The battle of Alma is our first foray into the Crimean War. The Russians, though outnumbered, have the heights with their guns entrenched in heavy fortifications. The British and the French suffer numerous communication breakdowns. The battle seesawed back and forth until a final assault by the Highland Brigade carried the day and the Russians broke and fled from the battlefield. Playing the Allies will test your ability to coordinate attacks via messengers. Playing the Russians will require skillful coordination of counterattacks.
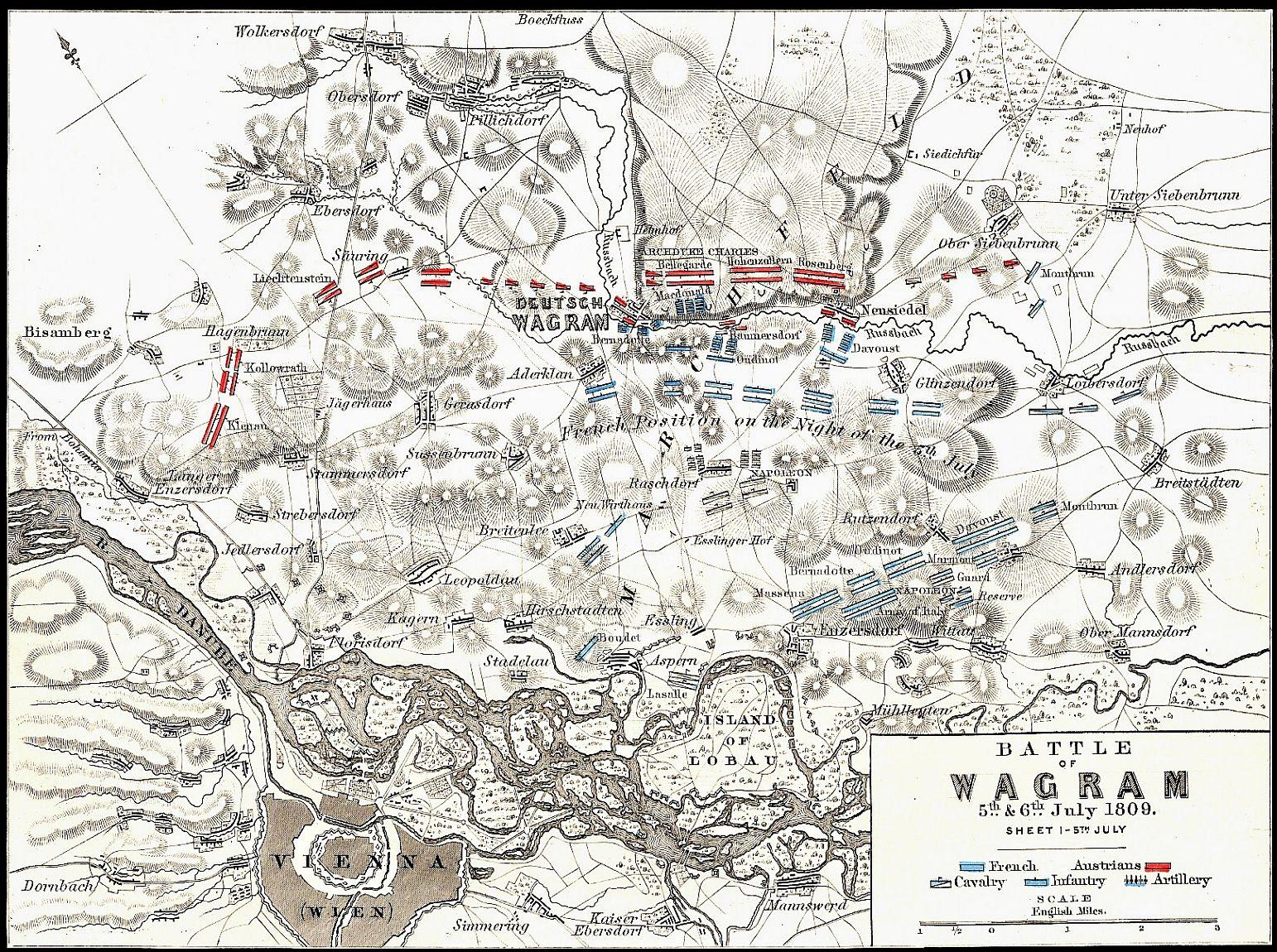
On May 21st and 22nd Napoleon had attempted to cross the Danube at Lobau Island only to be turned back by Archduke Charles. Now, after over a month of preparations and reinforcements, Napoleon was ready to try again.
We present two distinct scenarios for the battle of Wagram: the first representing the situation on July 5th and Napoleon’s second attempt at crossing the Danube and establishing a beachhead and the second the battle of July 6th in which Archduke Charles attempted a double envelopment of Napoleon’s army. Only Napoleon’s hastily created ‘grand battery’ of artillery, a desperate cavalry charge and a counterattack by MacDonald’s corps saved the day. The Austrians eventually broke and fled the battlefield and sued for an armistice which ended the 1809 war.
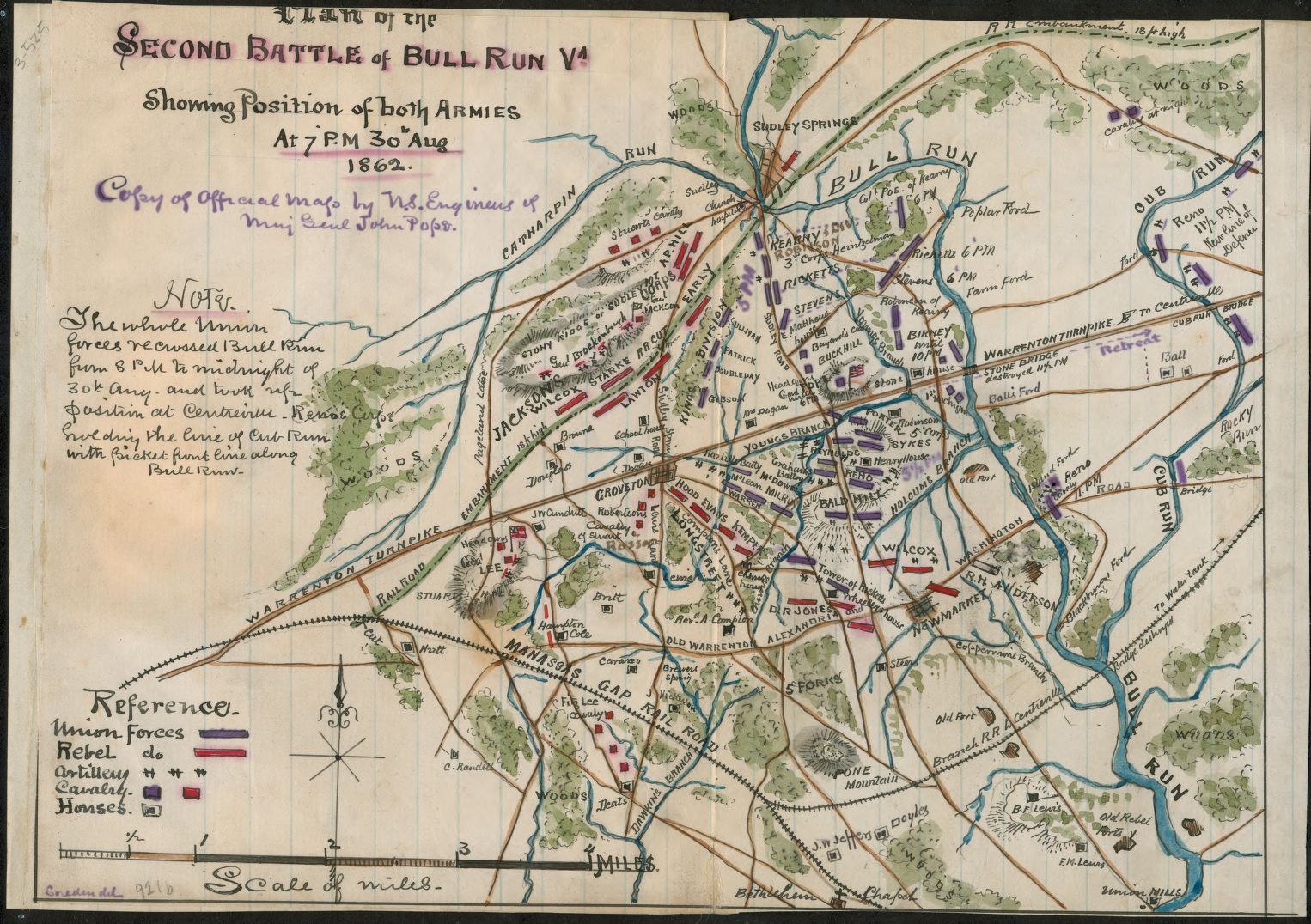
Plan of the second Battle of Bull Run Va. Showing position of both armies at 7 p.m. 30th Aug. 1862. From the Library of Congress. Click to Enlarge
After General George McClellan’s disastrous Peninsula campaign, President Lincoln appointed Major General John Pope to lead the newly formed Army of Virginia and was tasked with the missions of protecting Washington D.C. and clearing the Shenandoah Valley of Confederates. McClellan, who never responded promptly to orders even in the best of circumstances, simply ignored commands to begin transferring his army from the peninsula southeast of Richmond up to Pope in front of Washington. Lee, knowing that McClellan had a bad case of the ‘slows’ took advantage of his interior lines to rapidly move his forces north to destroy Pope before McClellan’s troops could reinforce him.
The battle on the old Mananas battlefield began on August 28, 1862 with Jackson (commanding the left wing) shelling the passing Union column of King’s division (which included the soon to be famous Iron Brigade). The Iron Brigade, though outnumbered, attacked and fought Jackson’s famous division to a standstill. However, Jackson’s attack was primarily a feint employed as a ‘fixing force’ for an envelopment maneuver; Longstreet’s corps was expected to appear on the Union’s unprotected left flank.
On the second day, August 29th, Pope attempted to initiate a double envelopment against Jackson. However, Longstreet had now appeared on the battlefield at exactly the wrong place for Pope’s envelopment maneuver. The day was marked with incredibly poor communications between Pope and his subordinates and ended mostly as it began with neither side gaining or losing much ground.
The third day, August 30th, began with Longstreet’s counterattack on the Union’s exposed left flank. Again, incredibly poor communications between Pope and his subordinates turned a bad situation into a disaster. Unlike the first battle of Bull Run, the Union army fell back on Washington in an orderly column through an extremely limited avenue of retreat over Bull Run.