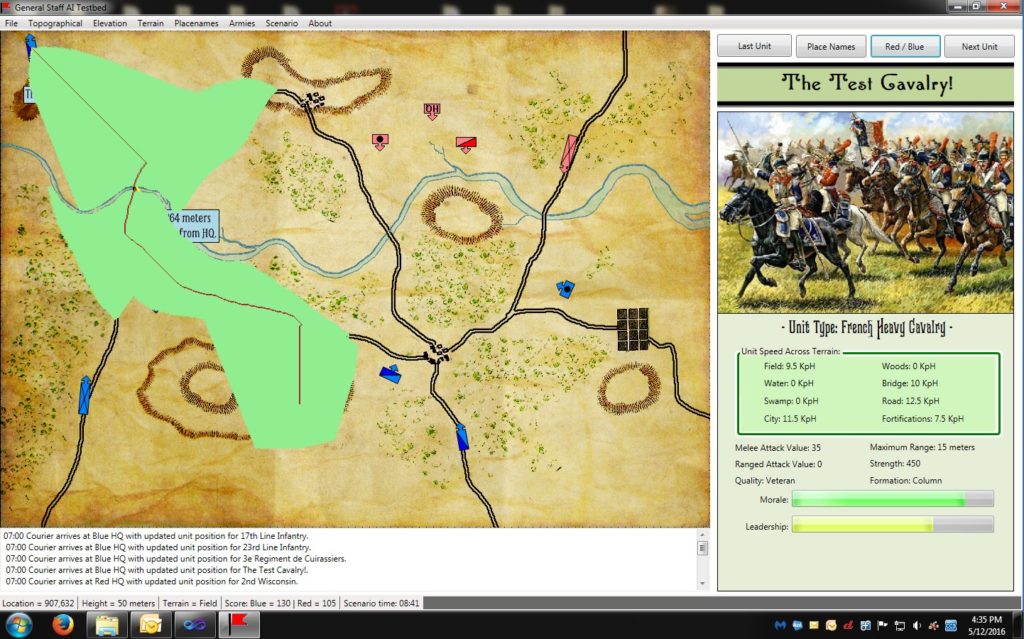
A screen shot showing traditional A* (pronounced A Star) pathfinding. The green areas are ‘nodes’ that the algorithm explored on its way to finding the optimal path (in Brown). Click on picture to enlarge to full size.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays an important role in wargame development; it’s what separates a good game from a great game. One of the most important algorithms employed in wargame AI is the A* (pronounced ‘A star’) pathfinding algorithm that was created in 1968 by Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson and Bertram Raphael. The paper describing it, A Formal Basis for Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths can be downloaded here. I did my doctoral Qualifying Exam on optimized pathfinding. My paper, “An Analysis of Dimdal’s (ex-Jonsson’s) ‘An Optimal Pathfinder for Vehicles in Real-World Terrain Maps'” can be downloaded here.

How long will it take for your orders to arrive at this unit? How long will it take for the unit to send a courier back to headquarters with its current location?
Pathfinding is important in wargames because it’s how units, under computer control, move around on the map. Also, and we’re announcing this for the first time here, when you give orders in General Staff a courier has to ride from your headquarters unit to the unit that is to receive your orders. Also, units on the battlefield that are not directly visible to the Headquarters unit (this is done with a 3D Bressenham line algorithm; more about this later) slowly begin to fade from view on the map. However, every hour a courier is dispatched from every unit to headquarters with an update on their position. As we can see from the information box, above, the courier will take 41 minutes to deliver the new position information to headquarters.
The top screen capture shows an implementation of the classic A* algorithm for calculating the optimal path from Blue’s headquarters unit to a far-flung cavalry unit. Note, this is an especially difficult path to calculate because the unit is across a river and there are only three bridges across. The A* algorithm performs perfectly but it is just too slow to be used with a real-time tactical wargame like General Staff. After some thought I wrote a major optimization of A* which we present here for the first time.
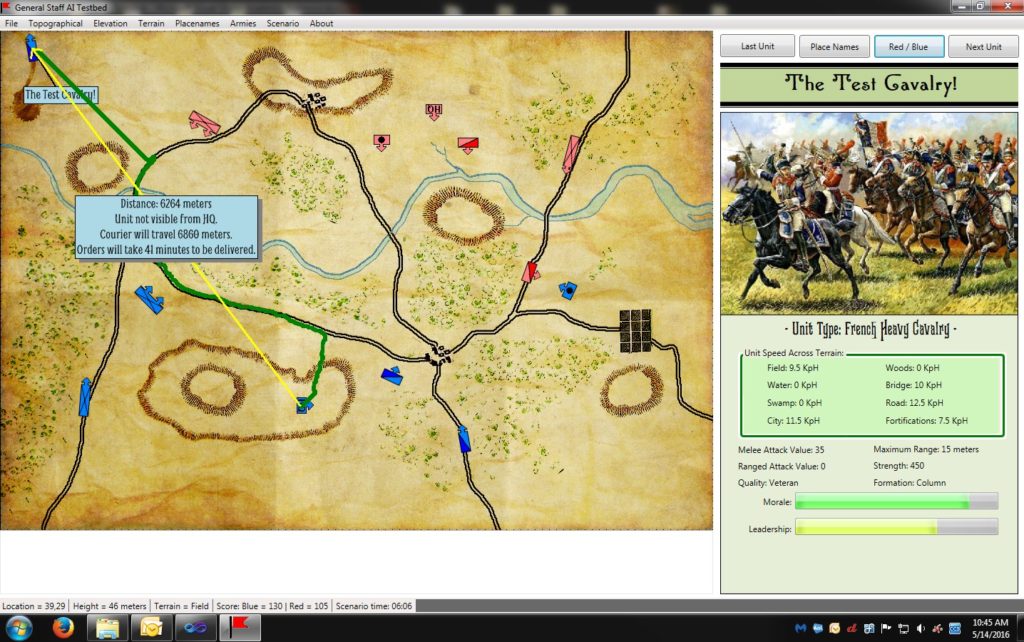
An example of the new EZRoadStar pathfinding algorithm created for General Staff. Compare it to the top screen capture which uses the classic A* algorithm. Click to enlarge.
Above is a screen shot of the results of the new EZRoadStar algorithm. It is almost identical to the original A* algorithm but runs thousands of times faster (my fellow computer scientists would probably prefer if I did some tests, wrote a paper and published the exact figures and I promise I’ll get around to that, some day).
In the screen shot, above, you can see the path of the courier (in green) from the Blue HQ unit to wayward cavalry unit. The new pathfinding algorithm, EZRoadStar, first looks for roads and then calculates how to get on and off the roads. This is much faster than the A* algorithm.

