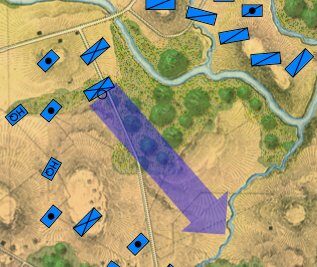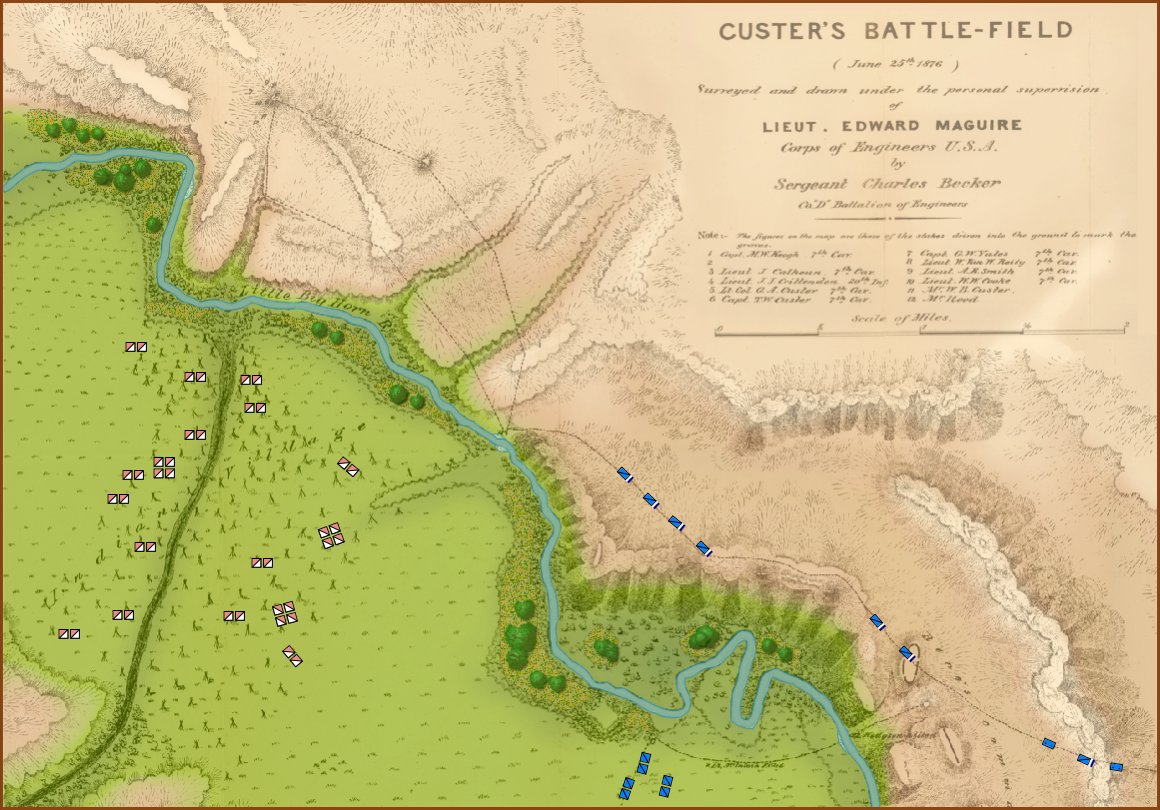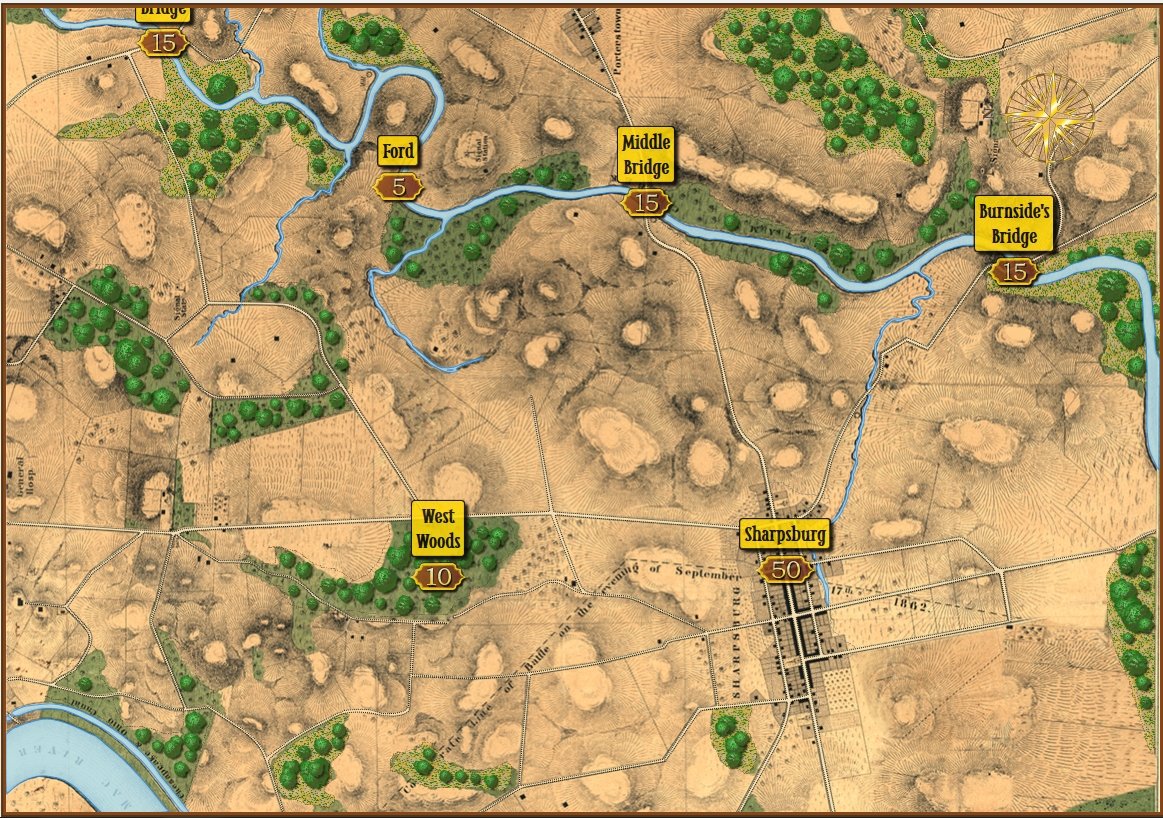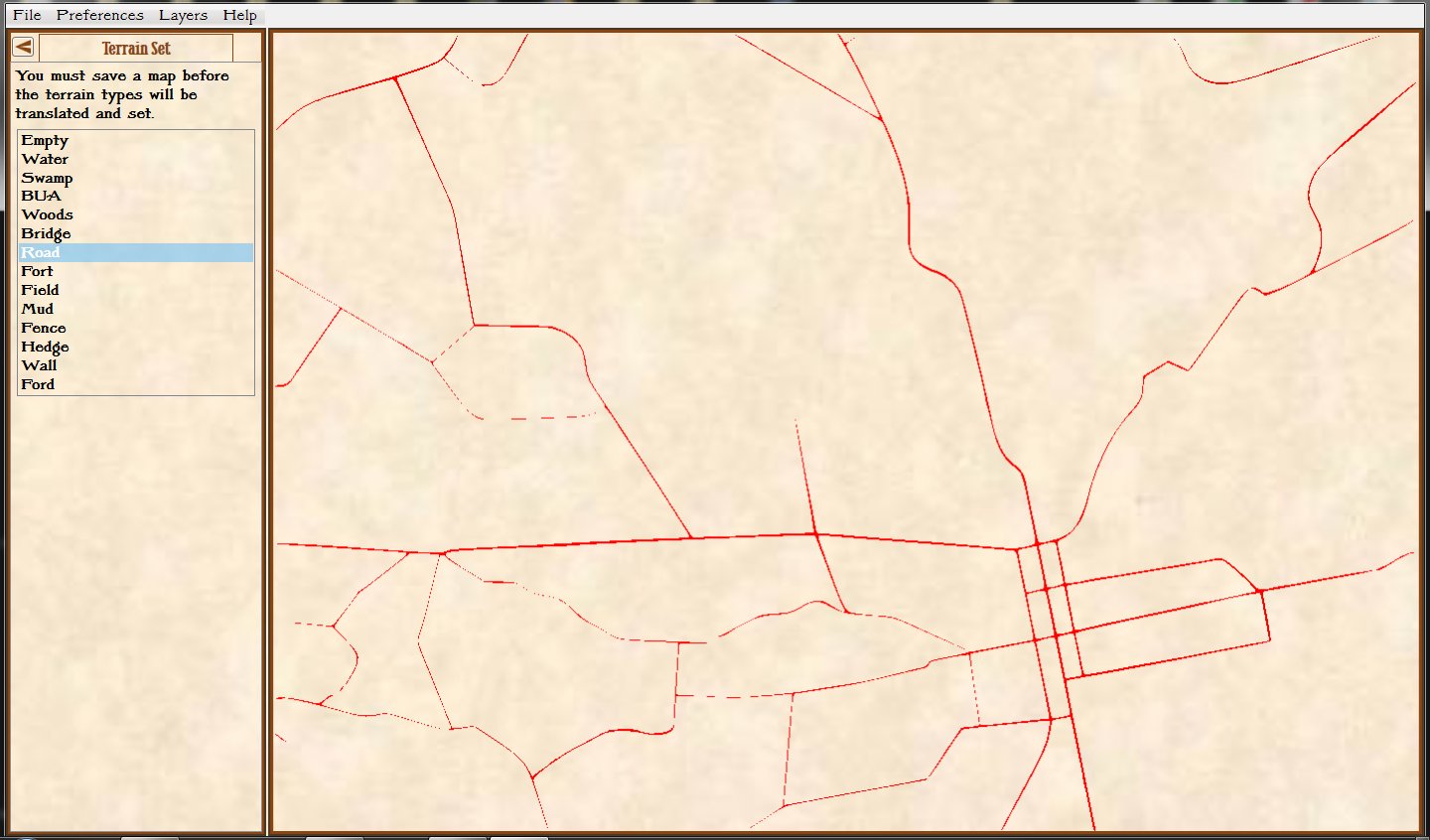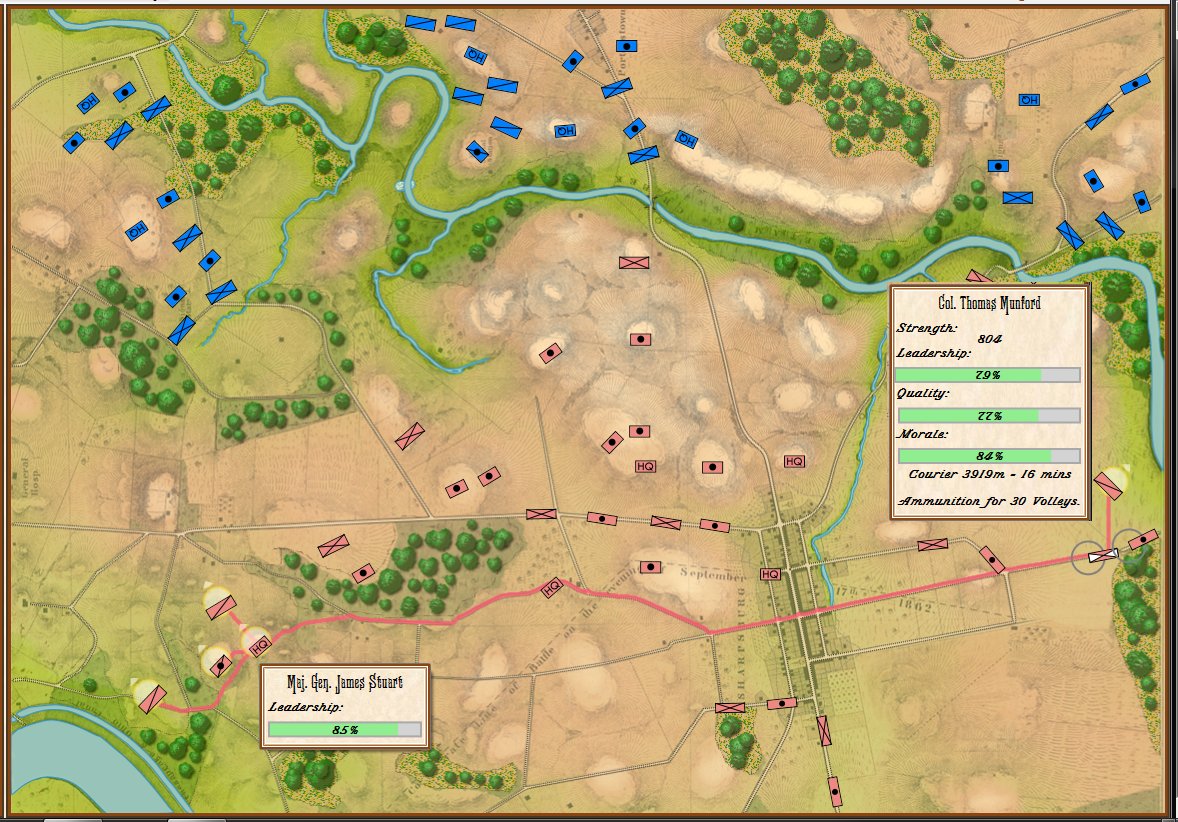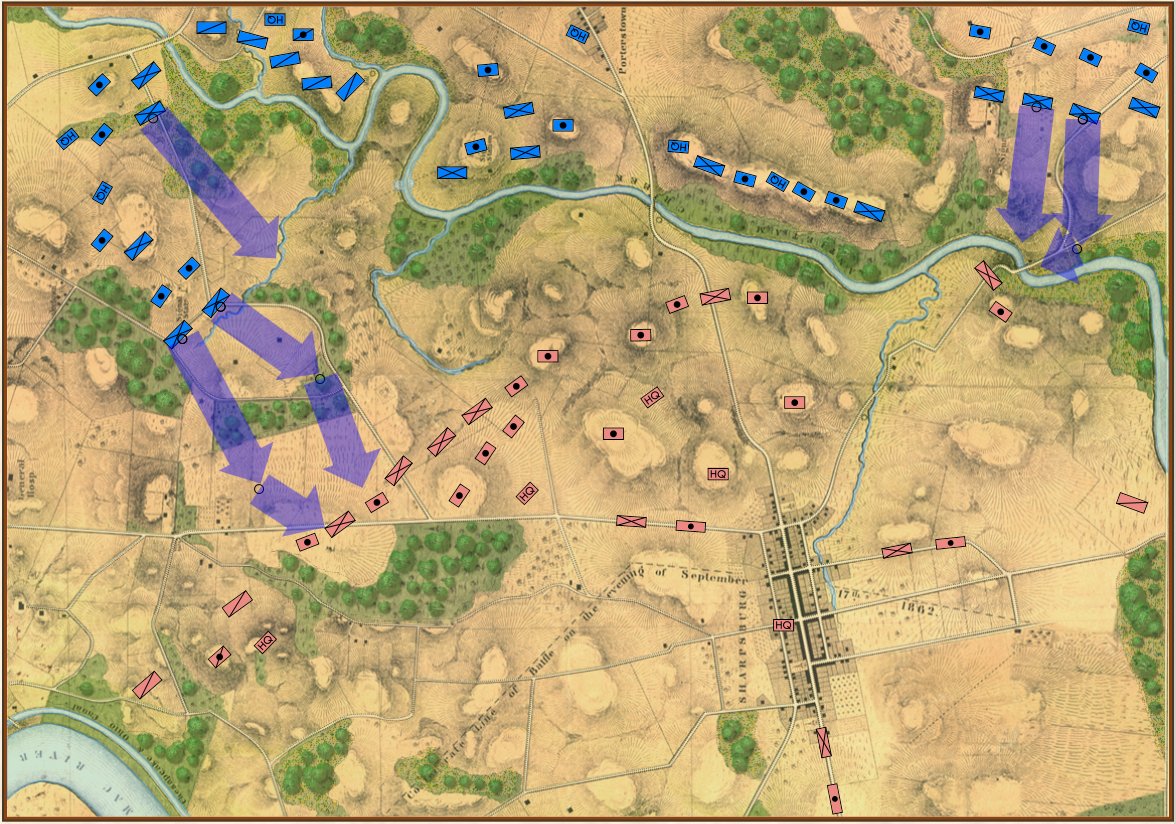
Screen shot showing unit movement arrows for the battle of Antietam scenario. Note how movement is stopped by the small creek in the upper left hand corner of the screen. Click to enlarge.
I‘m in self-quarantine. As many of you know, I had a bone marrow / stem cell transplant in 2014 followed by a year of intense chemo. I’m fine (all things considering) but my immune system took a beating. In 2014 H1N1 put me in the hospital for 3 days so I’m taking COVID-19 seriously as, uh, the plague. In a way, being cooped up in the house (the weather hasn’t been cooperating, either, as I had hoped to replace my daily gym workout with long walks with my dog, George) is a lot like a typical upper Midwestern winter: it’s what I call ‘good programming weather’. There’s not much else to do but hunker down and write code. So, obviously, I’m working on General Staff and I wanted to show you an update (above).
General Staff is being written in C# and Windows Programming Foundation (WPF). There are a number of technical reasons why this was a good idea but I’m not overly familiar with WPF and doing some basic things, like creating these transparent movement arrows, took far longer, and involved a lot more programming, than I thought it would. My partner on this project, Andy O’Neill, is a WPF rockstar; I’m a novice. I would much rather be working on the ‘under the hood’ stuff (like AI) but for the last week or so I’ve been working on movement arrows while Andy is busy with another project (the kind that pays the rent). Anyway, I’m very pleased about how they turned out. Please feel free to write me with comments.
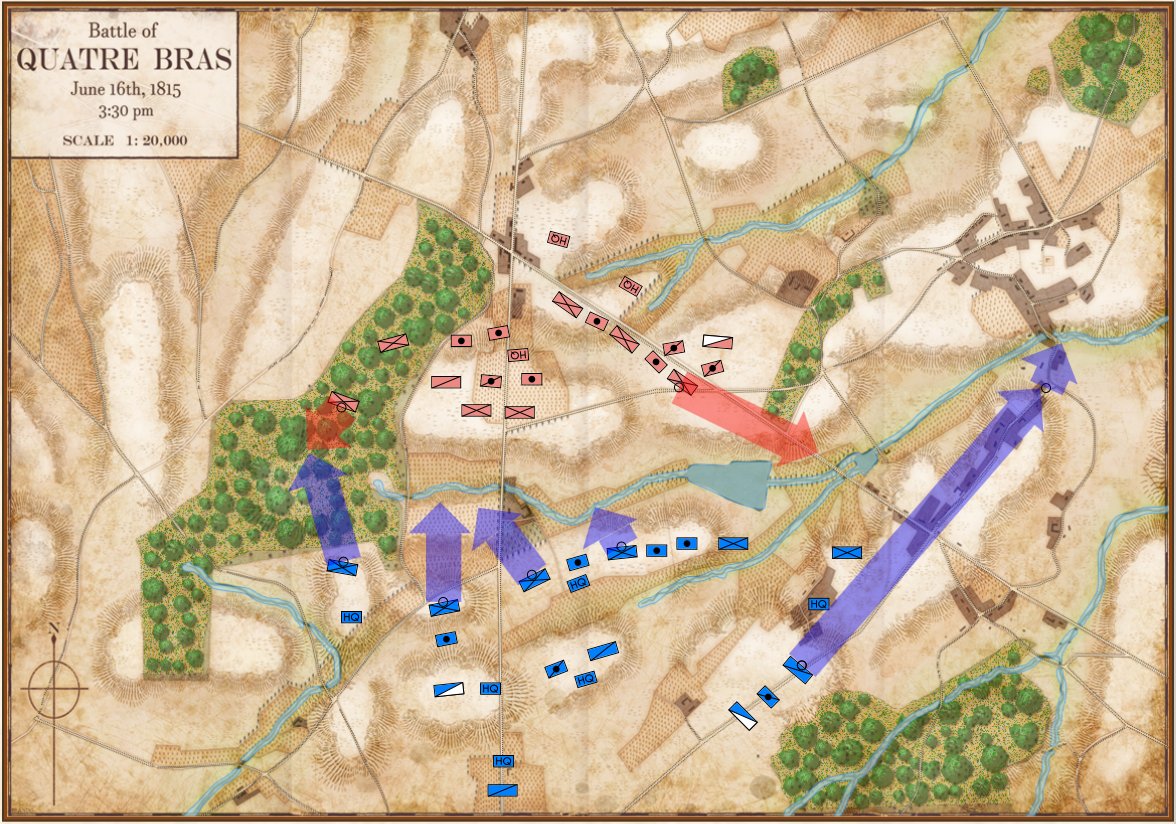
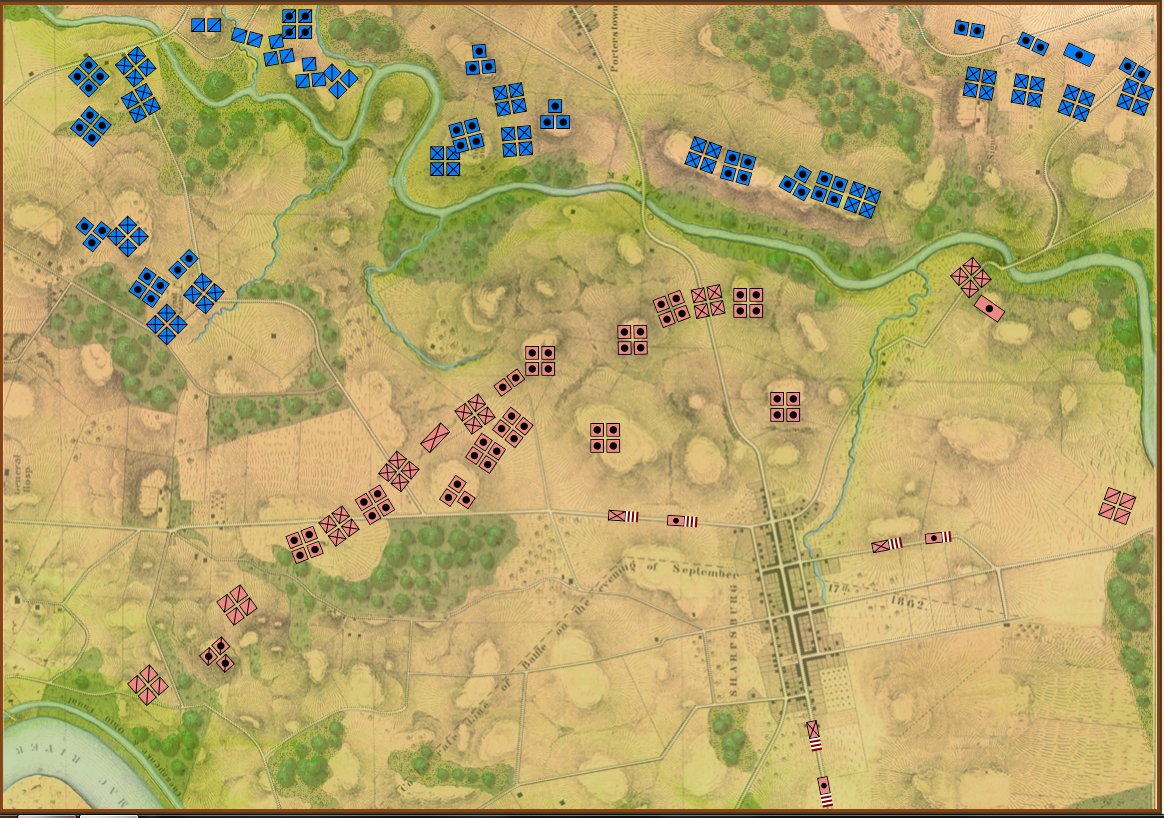
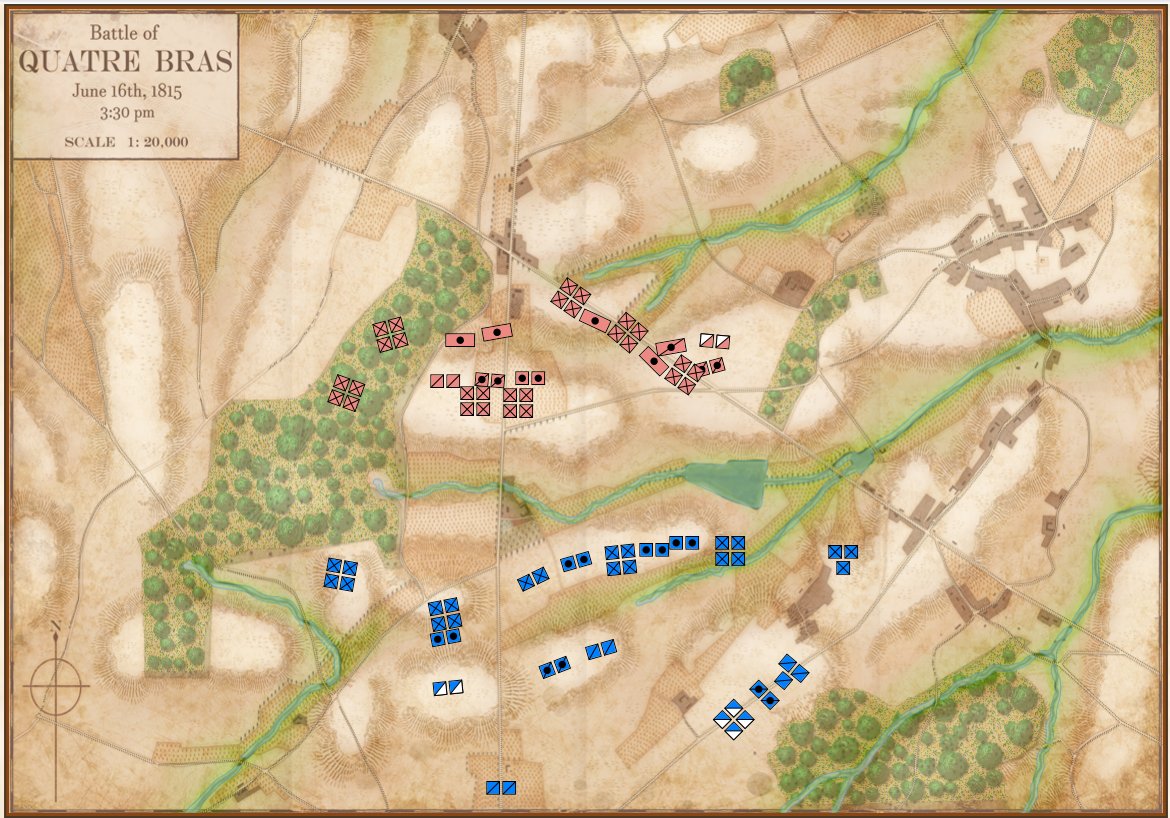
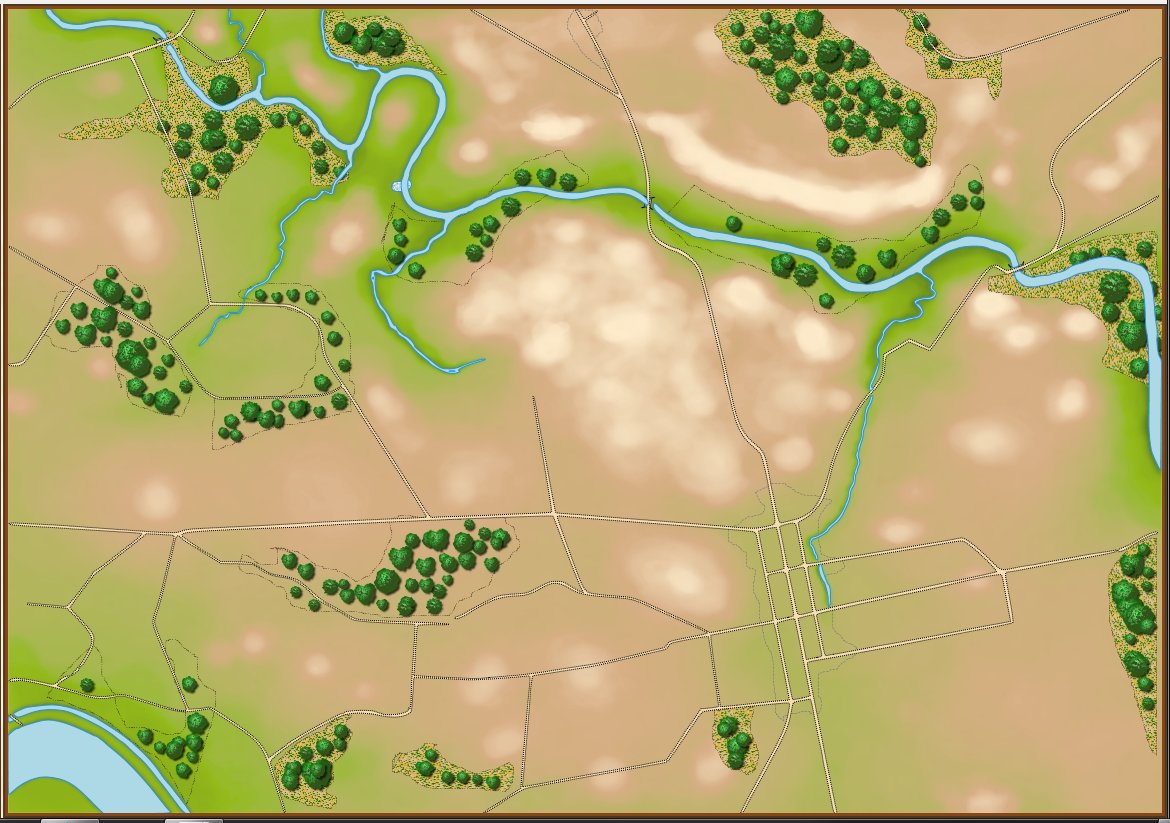
Movement arrows for units at Quatre Bras. Note how blue units are stopped by the stream feeding the large pond. Click to enlarge.
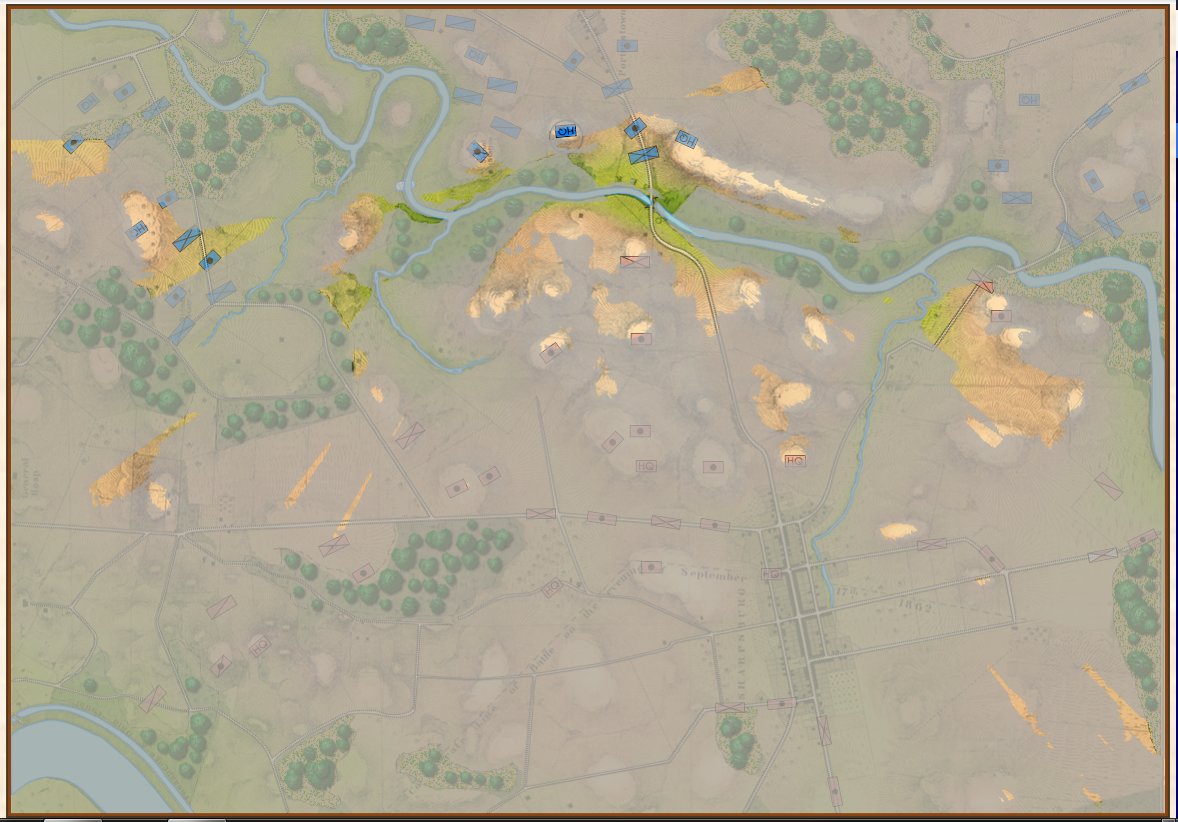
But, I also discovered a very interesting problem while testing these movement routines: our maps are too good! If you look at this detail (right) from the Antietam screen capture (above), you’ll see that movement is stopped when it encounters a tiny creek. I’ve walked that area of the Antietam battlefield and that little creek (well, I think it would be more properly called a ‘crick’) wouldn’t stop a division moving forward. However, the movement validation routines stop units from crossing bodies of water (except in column formation while crossing a bridge or a ford). Ed Kuhrt, who digitized these great maps and copied every small detail was, perhaps, too precise. Definitely better to err on the side of being too precise when it comes to maps, Ed.
We’re seeing the same thing at Quatre Bras (above): the little streams that feed Materne Pond (Etang Materne) are also stopping the French from attacking. I haven’t been to Quatre Bras but I know the French crossed the small streams to attack the Anglo-Allied army’s positions.
Luckily, fixing this is easy. If you have done any work with the General Staff Map Editor you know that erasing terrain features, like water, is quick.
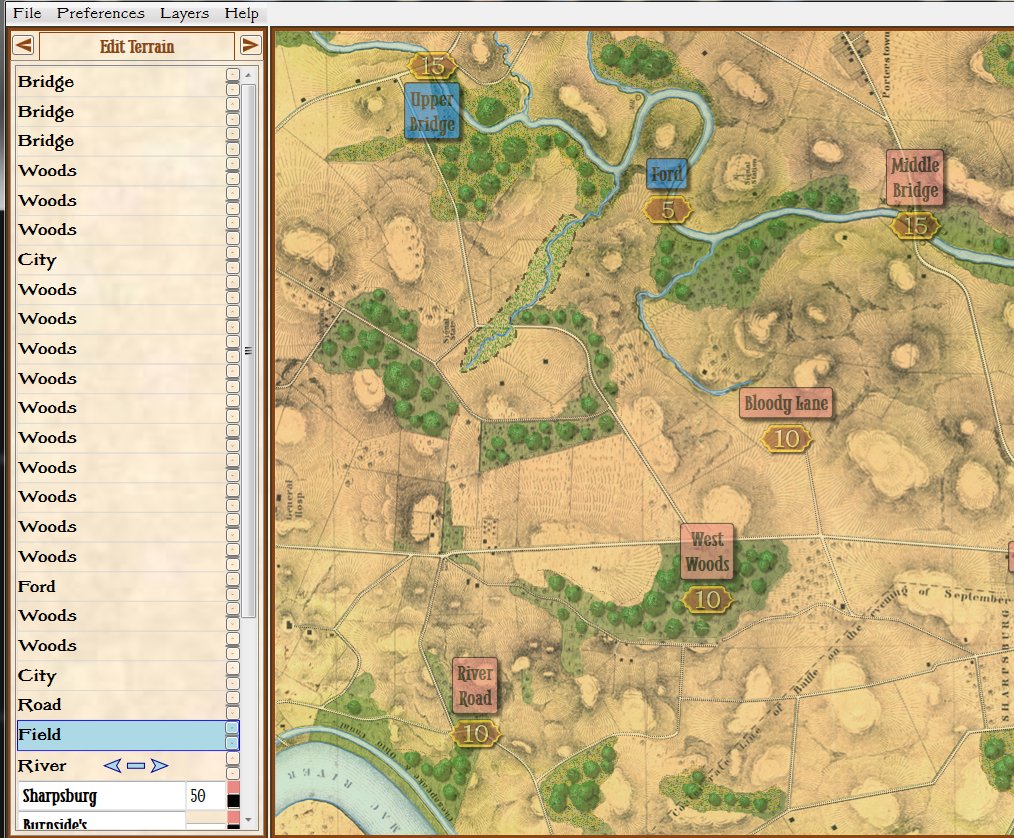
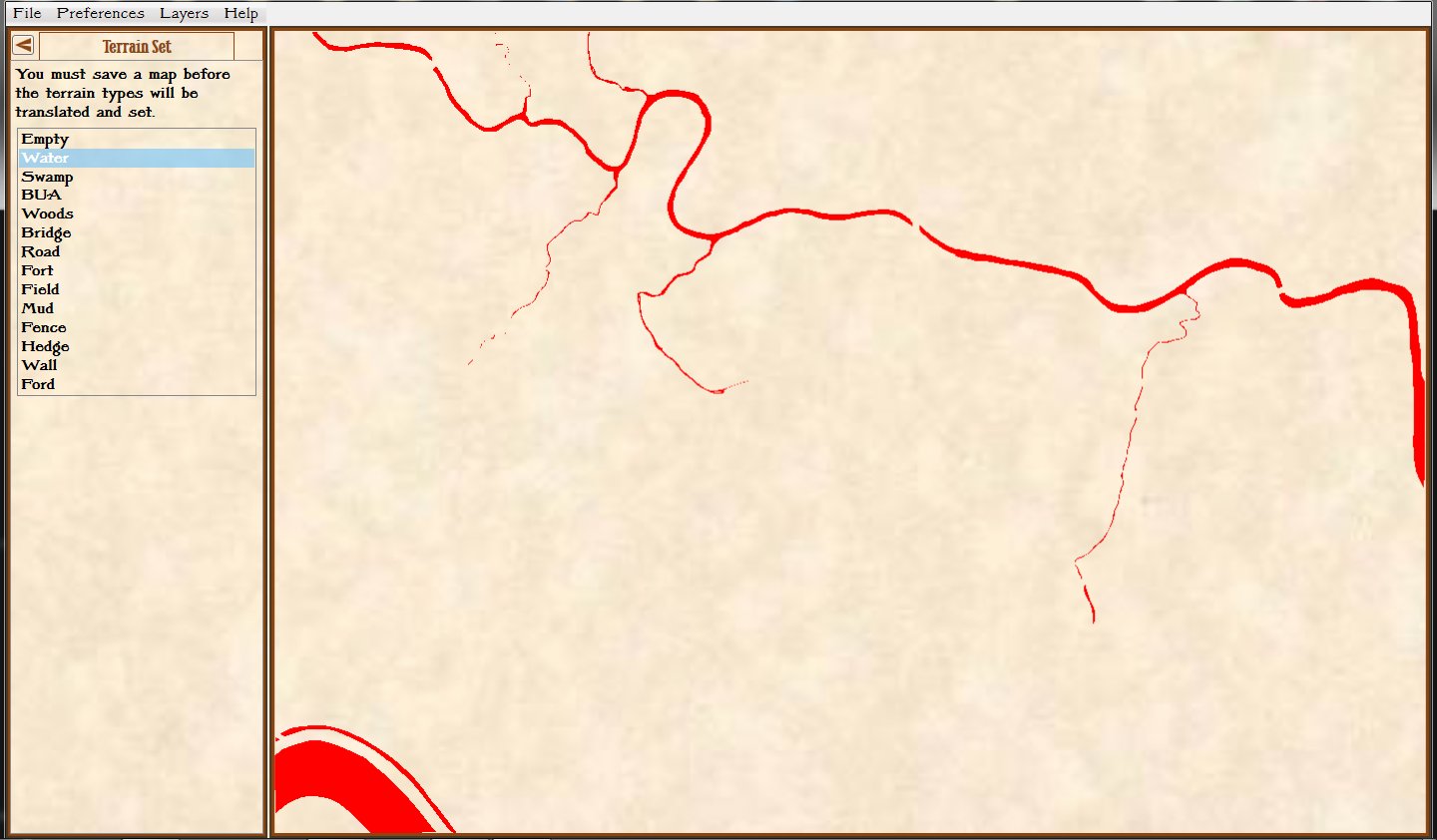
Removing the water in the little stream that feeds Antietam Creek by placing a ‘field’ over the water. Note that the ‘Field’ object is ‘above’ the ‘River’ object on the left Edit Terrain tab. Screen shot. Click to enlarge.
In the above screen shot we’ve opened the Antietam map in the General Staff Map Editor and drawn a ‘Field’ over the ‘crick’ that kept the Union forces from advancing. Note that both the Field and the River are objects and whichever object is higher in the list on the left ‘overwrites’ lower objects. If, for whatever reason, we wanted to restore the water in the creek we could either delete the Field or move it lower down the list than the River object.
Edit: After originally posting this, some readers (see comments, below) suggested that units crossing a small stream should suffer a movement penalty. This is absolutely correct. Instead of ‘painting’ with ‘field’ terrain, I should have used ‘mud’. This allows for a movement penalty (set in the Scenario Editor).
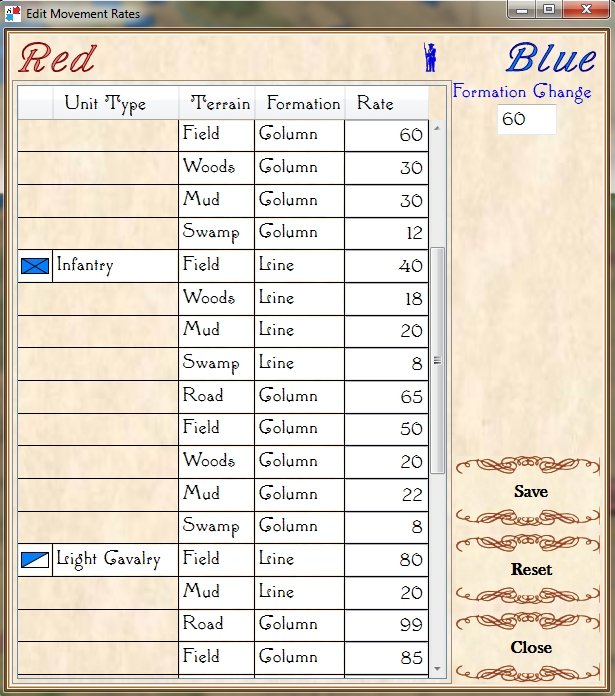
Adjusting unit type speeds across various terrain types in the General Staff Scenario Editor. Screen capture.
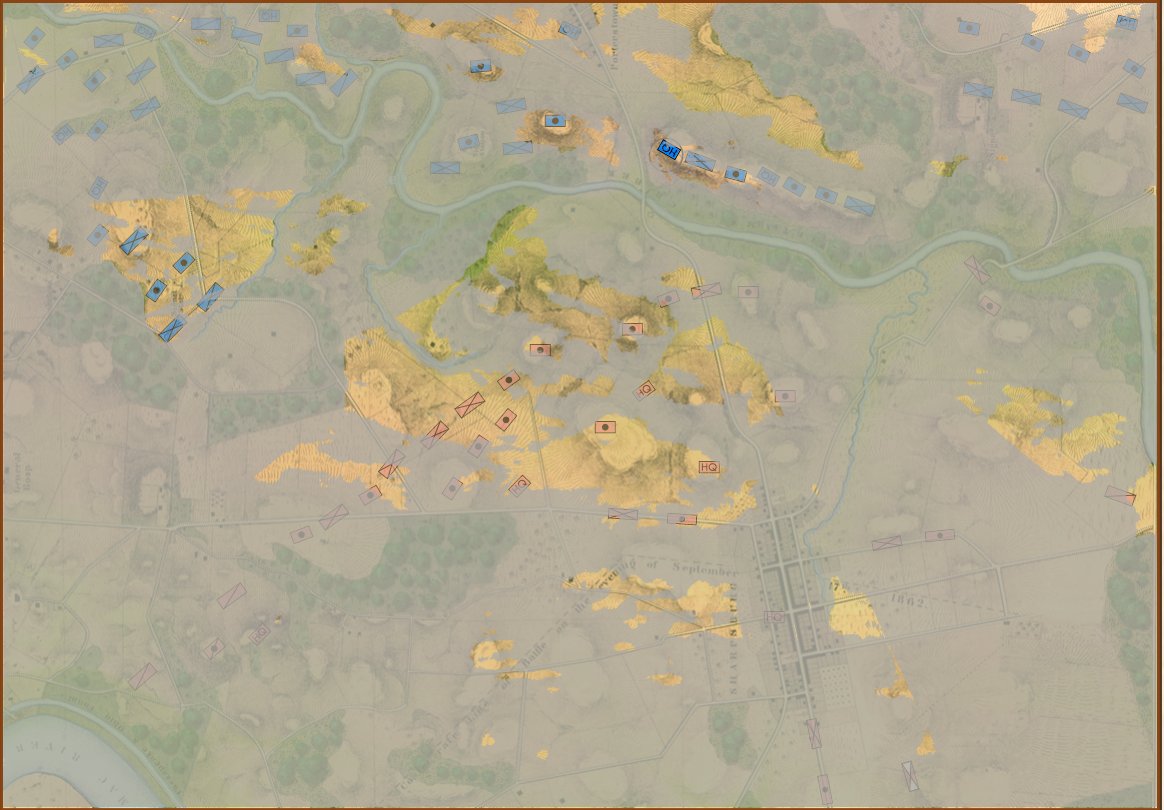
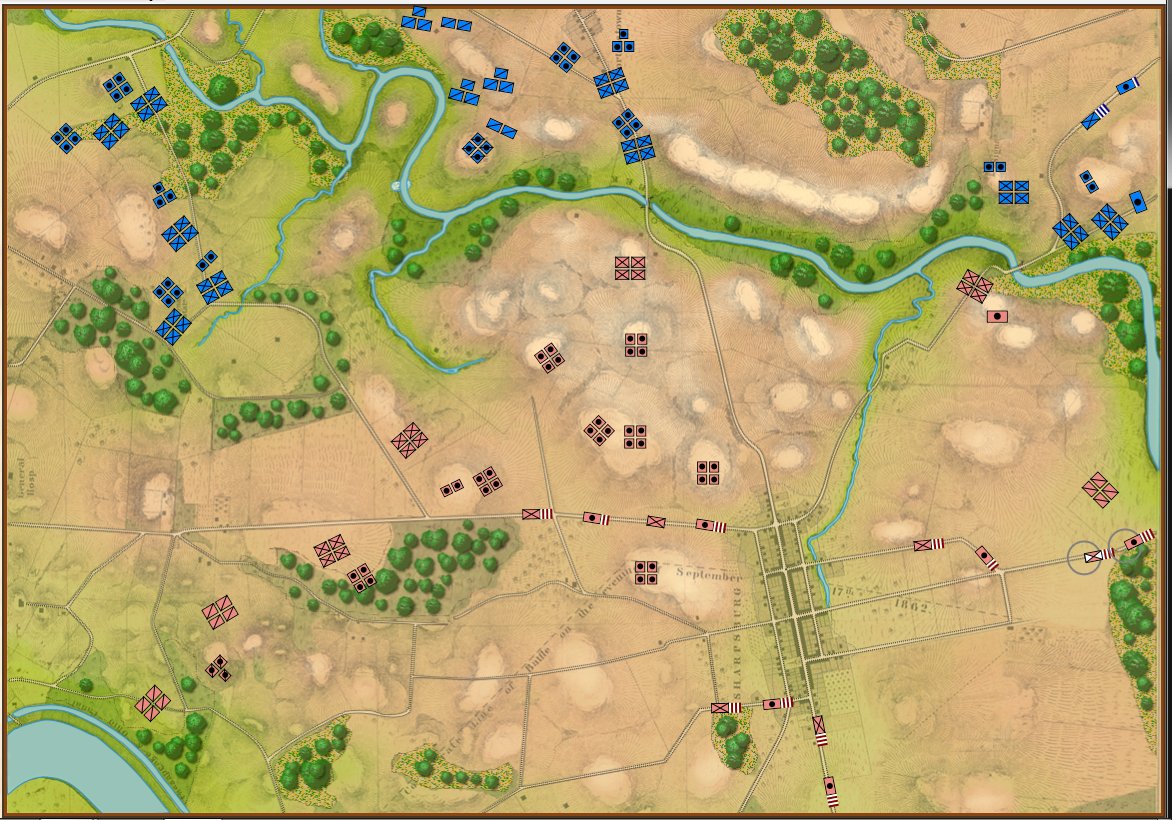
And now that that obstacle to movement has been eliminated the I and XII Union Corps can advance:
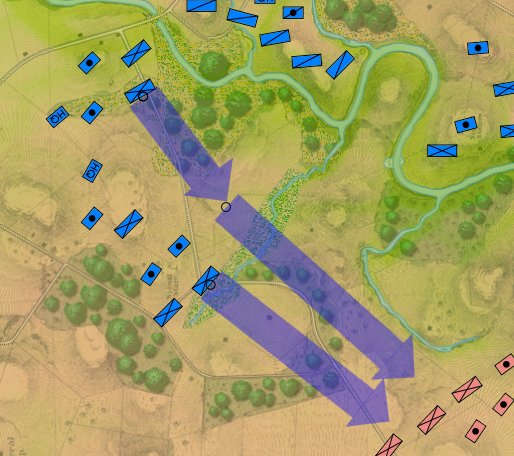
Now that the water has been removed from the little stream feeding Antietam Creek the Union forces can advance again. Screen shot.
As always, I would love to hear any comments or feedback that you may have.